If you want to get the values of Environment Variables in AWS Lambda using Node.js runtime follow the instructions below.
Node.js Code to Access Environment Variables
To access the Environment Variables of Lambda Functions using Node.js or javascript simply use the code below.
const environmentVariable = process.env.ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLELet’s say that my environment variable has a name of DB_USER, I will use the code below to get its value.
const dbUser = process.env.DB_USERIt’s actually the same way how we access Environment Variables when we code in our local computer.
Sample Lambda Code to Access Environment Variables
I setup the following environment variables in my AWS Console.
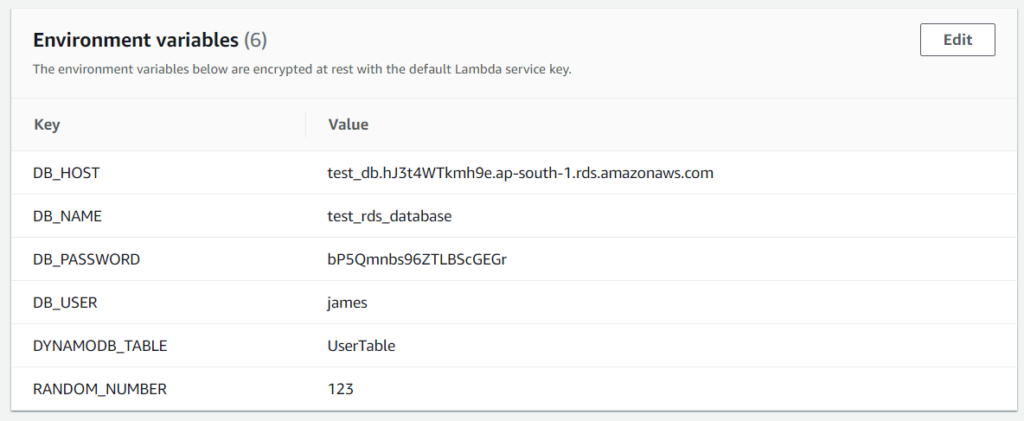
Below is the Javascript code to access the environment variables we set in the Lambda Function.
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const dbHost = process.env.DB_HOST
const dbName = process.env.DB_NAME
const dbUser = process.env.DB_USER
const dbPassword = process.env.DB_PASSWORD
const dynamoDbTable = process.env.DYNAMODB_TABLE
const randomNumber = process.env.RANDOM_NUMBER
console.log('dbHost:', dbHost)
console.log('dbName:', dbName)
console.log('dbUser:', dbUser)
console.log('dbPassword:', dbPassword)
console.log('dynamoDbtable:', dynamoDbTable)
console.log('randomNumber:', randomNumber)
};Here is the output of the AWS Console.
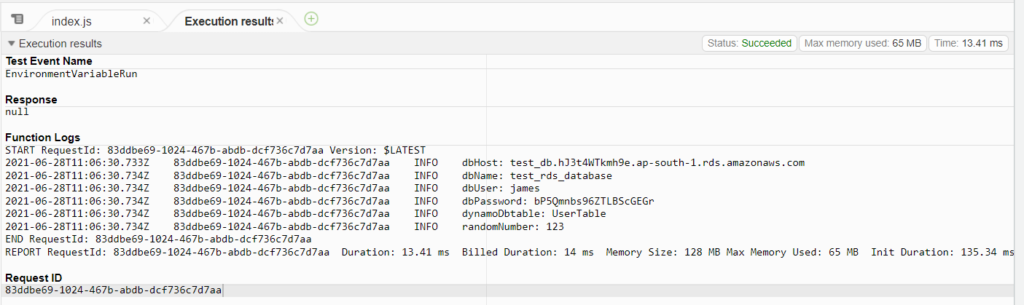
Environment Variables are Strings
In the example above we have the environment variable named RANDOM_NUMBER with a value of 123.
When we get the value of the RANDOM_NUMBER environment variable using process.env it will always return a string.
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const randomNumber = process.env.RANDOM_NUMBER
console.log(typeof randomNumber) // output 'string'
console.log(randomNumber)
}If you want to get the value of RANDOM_NUMBER as number or integer value then use parseInt to convert it to an number type.
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const randomNumber = parseInt(process.env.RANDOM_NUMBER)
console.log(typeof randomNumber) // output 'number'
console.log(randomNumber) // output 123
};Let’s say that my RANDOM_NUMBER environment variable has a value of 123.456. Converting this to a number using parseInt will automatically drop the decimal places.
If you want to get the value of RANDOM_NUMER without losing the decimal places then you should use parseFloat.
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const randomNumber = parseFloat(process.env.RANDOM_NUMBER)
console.log(typeof randomNumber) // output 'number'
console.log(randomNumber) // output 123.456
};Show all Environment Variables in Node.js Lambda Function
If you want to see all the Environment Variables and its values visible on your Node.js Lambda Function use the code below.
exports.handler = async (event) => {
console.log(process.env)
};Here is the output of the console.log(process.env). The output below includes the test Environment Variables that we used earlier.
{
AWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_VERSION: '$LATEST',
DB_HOST: 'test_db.hJ3t4WTkmh9e.ap-southeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com',
DB_NAME: 'test_database',
AWS_SESSION_TOKEN: 'IQoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEK7//////////wEaCmFwLXNvdXRoLTEiRzBFAiAh8nFYW6Z0CUfpPWu3EkT6coHKWEEDL7kfdz5aD9gvTAIhAPYwaBbKnE8DKKKKgT95m35pU9wXFj2TEABVeV7r9gS8KpoCCIf//////////wEQAhoMNDAwMDUzMDExMTEwIgxRoJ2bXMSi9datOnkq7gF4JkCxMMd32Zf9FC9O+POwClAKql5kTyuME/4h3XzbB7daiE8eekiiiC99wEKYDN3u0VHwc0c4EU5oyIsJgQviemFRnppgRE8FAQHz1VyaAjqyH8WZjvdn+y+Xk6CWuWp8uhIMQoVqNdDO1bs4U3tzp0+IbxskLNExM9rtYywpPkAhyhdPbuHvDWmqt0Pw3cPcUWYbL6baCYN7rHxO6LmMBYtZS2ElRGvdML+BY/6XIYv8fcRSlp3lACalsAtz/P+hEG6nmO+hY0gHzeDGZ0zTAVFRf2vlg75rp7Xkq00Hi0A1V+Wawy+h05zcRrz6MKb26oYGOpoBjHmH/PvHoVr5cXOAm1jaAd8YRaE0kkIt+j4GU7aLfVfZtASIMB+y9lj+3jELD4J8kZ5qZAt13aygwa4FfpFwJYkqItwCUPJLnW4rTkSqa+JVM3jtUFk5H8+q/rRfWFPP6R09rV7qWoj5EwDSyy2QSlVG2PJ0tU9b1csMCr+OLx0VtGLQHHcqctyXKIgTKEPrIrXldGnPHdqdKw==',
LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT: '/var/task',
LD_LIBRARY_PATH: '/var/lang/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/var/runtime:/var/runtime/lib:/var/task:/var/task/lib:/opt/lib',
AWS_LAMBDA_LOG_GROUP_NAME: '/aws/lambda/testFunction',
AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API: '127.0.0.1:9001',
AWS_LAMBDA_LOG_STREAM_NAME: '2021/06/29/[$LATEST]3285d572f4634e4eb1a74e6ff7eafd3b',
AWS_EXECUTION_ENV: 'AWS_Lambda_nodejs14.x',
AWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_NAME: 'testFunction',
AWS_XRAY_DAEMON_ADDRESS: '169.254.79.2:2000',
PATH: '/var/lang/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin/:/bin:/opt/bin',
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: 'ap-south-1',
PWD: '/var/task',
DB_PASSWORD: 'bP5Qmnbs96ZTLBScGEGr',
RANDOM_NUMBER: '123',
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: 'kU5gBB596$lrIRzpZP7nP&6SX&%ZKtG$ssrJm2D*',
LANG: 'en_US.UTF-8',
LAMBDA_RUNTIME_DIR: '/var/runtime',
AWS_LAMBDA_INITIALIZATION_TYPE: 'on-demand',
DYNAMODB_TABLE: 'UserTable',
NODE_PATH: '/opt/nodejs/node14/node_modules:/opt/nodejs/node_modules:/var/runtime/node_modules:/var/runtime:/var/task',
AWS_REGION: 'ap-south-1',
TZ: ':UTC',
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: 'PUMLUQBIJU3E8PNK0CIA',
SHLVL: '0',
_AWS_XRAY_DAEMON_ADDRESS: '169.254.79.2',
_AWS_XRAY_DAEMON_PORT: '2000',
DB_USER: 'james',
AWS_XRAY_CONTEXT_MISSING: 'LOG_ERROR',
_HANDLER: 'index.handler',
AWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_MEMORY_SIZE: '128',
_X_AMZN_TRACE_ID: 'Root=1-60dabb26-025c1aa44bf92db6674d4dee;Parent=43e18be83fa6935d;Sampled=0'
}If you want to know more about each of the Environment Variables defined by AWS Lambda you can visit AWS docs here.
I hope you learned how to access AWS Lambda Environment Variables using Node.js or Javascript.
thanks,
are those in the app settings?
or the stage