Editing configuration values inside the code is a high risk for error since there is a high chance that not only the values that you are changing you will change, you might even delete a letter or edit a line. In order to avoid this risk, you want your code to be able to accept configuration values at run time. This is extremely useful when developing codes on different environments like development, testing and production.
With AWS Lambda you can reuse your code on different environments using the Environment Variables.
Below is the way to use Environment Variables on AWS Lambda Console using Python 3.6.
Note: This is the same way to use Environment Variables on Python 2.7 and Python 3.7.
Environment Variables Setup
The Environment Variables section can be found under the Function Code section.
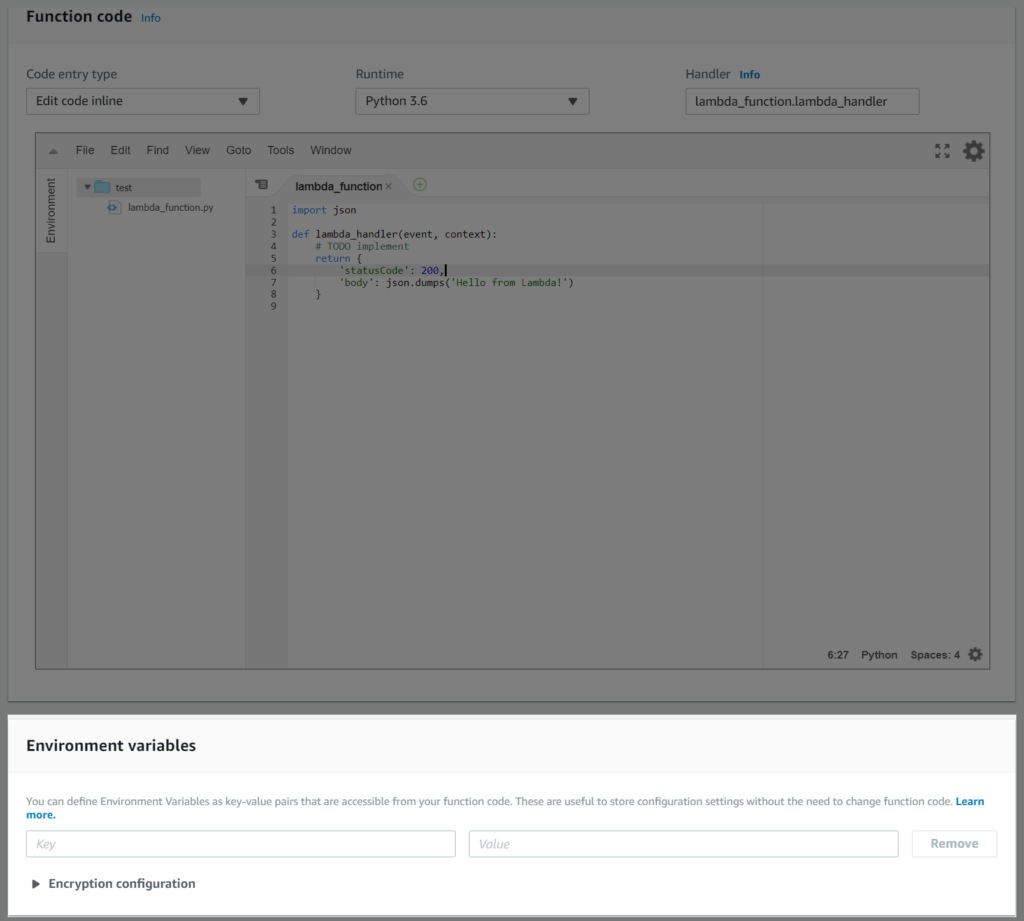
Environment Variables are Key/Value Pairs. The Key is what you will use on your Lambda Code, to access its Value.
Let us use the following Key/Value Pairs for this example.
| Key | Value |
| dbHost | test_db.hJ3t4WTkmh9e.ap-southeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com |
| dbUser | james |
| dbPassword | bP5Qmnbs96ZTLBScGEGr |
| dbName | test_database |
Here is a screenshot of the Environment Variables with the Key/Value Pair above.
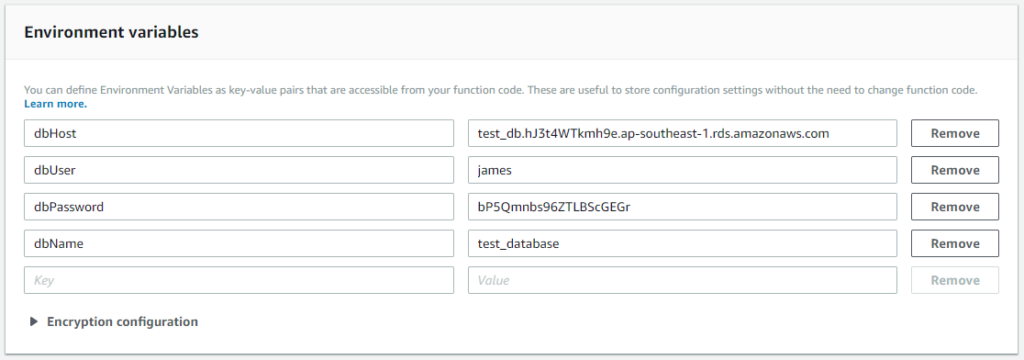
You can also add Encryption configuration but for the purpose of this introductory post I will not deep dive on this.
Lambda Code
To access the Environment Variables on your Python Lambda Code we need to import the os module.
import osThen on our lambda code we use os.environ to access the value of the Environment Variable.
os.environ['KeyName']The above will return the Value of the stated Environment Variable KeyName.
Below is the code I used to retrieve the environment variables.
def lambda_handler(event, context):
DB_HOST = os.environ['dbHost']
DB_USER = os.environ['dbUser']
DB_PASSWORD = os.environ['dbPassword']
DB_NAME = os.environ['dbName']
print('dbHost:', DB_HOST)
print('dbUser:', DB_USER)
print('dbPassword:', DB_PASSWORD)
print('dbName:', DB_NAME)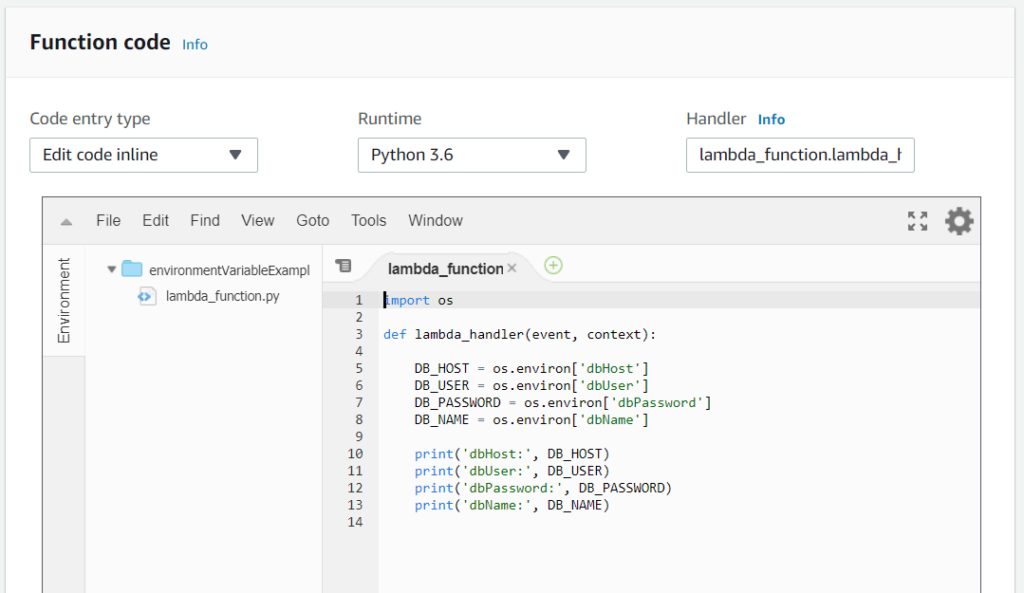
Testing the Lambda Code
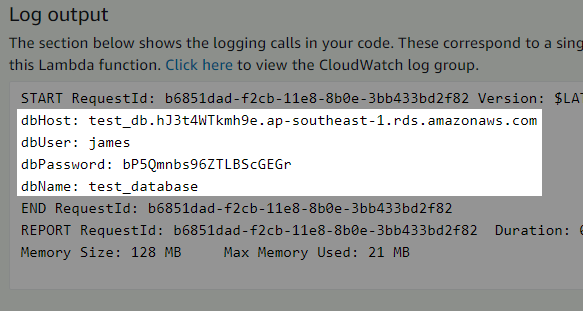
Here is the result when I tested it.
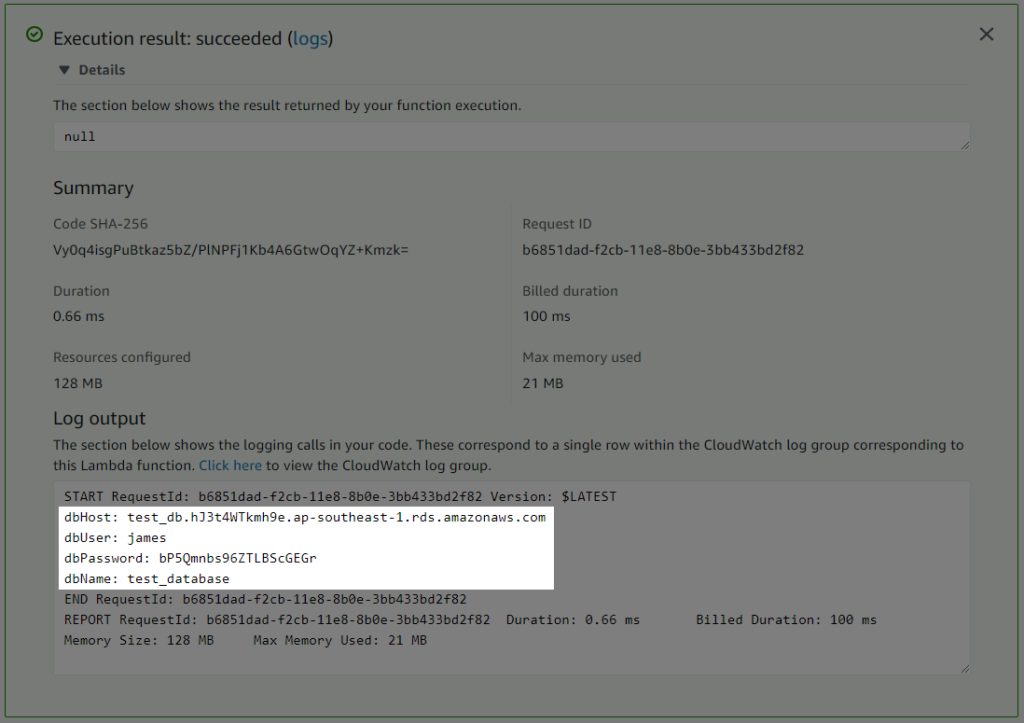
Closer screenshot on the Log output.
Note on os.environ
The os module is a way for python to use operating system dependent functionality. See python documentation here.
os.environ is a mapping object representing the environment. It is actually a sort of dictionary type in Python so you can access the Key/Value Pairs with brackets [], just like a Python dictionary. For more information on os.environ you can check the documentation here.
If you want to see what os.environ data looks like when you run it in Lambda try using the Python Code below on your Lambda Code.
import os
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
DB_HOST = os.environ['dbHost']
DB_USER = os.environ['dbUser']
DB_PASSWORD = os.environ['dbPassword']
DB_NAME = os.environ['dbName']
print('dbHost:', DB_HOST)
print('dbUser:', DB_USER)
print('dbPassword:', DB_PASSWORD)
print('dbName:', DB_NAME)
print('os.environ')
print(json.dumps(dict(os.environ), indent=4))As much as I want to show you the output of my os.environ object, I cannot as this has a lot of security details in it that would compromise my AWS account security.
Anyways, I hope you learn how to use Environment variables on AWS Lambda Python.
I want to thank you for your post here which shows how to output all the AWS environment variables, and also using the dict() method. It helps me to solve my problem here.
Hi Sy, great to hear that the post helped you. ^_^
Can you tell us how to add environment variables during (runtime) code execution
Hi Srii, can you tell me more about your use case for adding Environment Variables during (runtime) code execution?
I think it would be better to pass the value of the variable as a parameter to a function. If not you can use a Global Variable in Python Lambda Function.
I want to pass parameters and tags from API Gateway. please discuss how to modify this lambda function to get parameters
thank you very much for the wonderful article
you’re welcome very much 🙂